TECHNOLOGY
The amount of sunlight that strikes the earth's surface in an hour and a half is enough to handle the entire world's energy consumption for a full year.
A solar power system is a system that utilizes this sunlight and helps to carry out the process of converting the sunlight into DC current and then carrying the energy to the place of use .
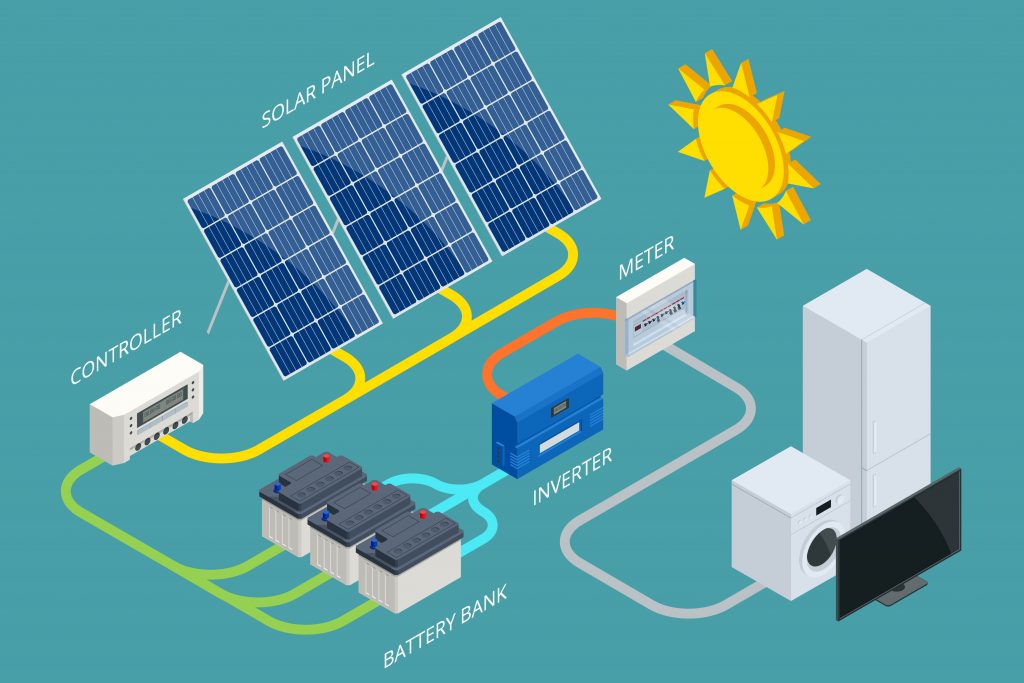
A solar power systems usually consists of 3 main components:
•Solar PV Panels
•Solar Inverters
•Solar Batteries
Solar PV Panels
Solar Panels
are devices that capture the sunlight to convert it into electricity. These panels consist of a number of PV cells, which are made of silicon, connected together. These panels are in turn connected to one another to form an array, which helps to increase the amount of sunlight that is captured and converted into energy effectively.
Solar Inverter
The energy that is created in the solar panel is in the form of DC current. For this current to be used in everyday applications like powering homes and offices, it needs to be converted into AC current. The solar Inverter is a device that helps to convert the produced DC current into usable AC current.
There are many types of inverters such as the String Inverter, Micro Inverter, etc. that are used in different places according to the need of the situation. There are also devices called Power Optimizers which can be attached to the back of a solar panel, that help us control and monitor each individual panel and ensures that they are performing at maximum capacity.
Solar Batteries

Solar Batteries
are devices that can be charged up to store energy. These are connected to solar systems so that they can charge and provide power at times when the required power is not available or if the panels are not able to perform their work effectively (periods of the day when sunlight is not available, like cloudy days or night-time).
There are 3 different kinds of solar power systems:
On-Grid System:
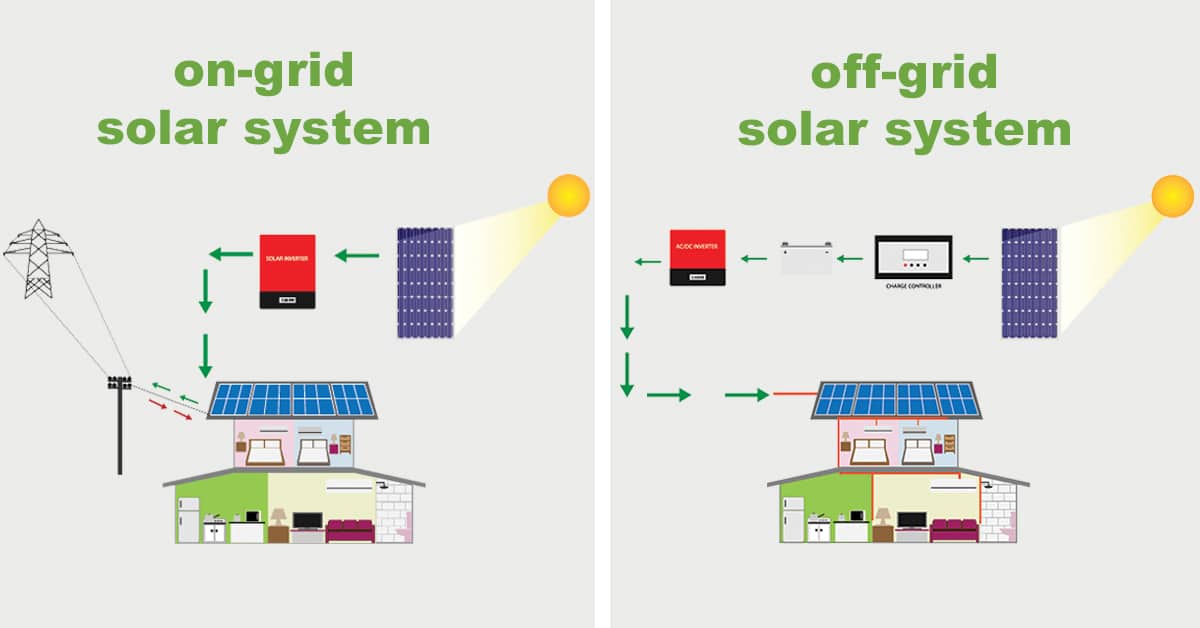
On-grid or grid-tie solar systems are ones that do not use batteries but use micro-inverters and are connected to the public electricity grid. These systems are the ones that are most commonly used in homes and businesses.
Any excess solar power that you generate is exported to the electricity grid and you usually get paid a feed-in-tariff (FiT) or credits for the energy you export.
Unlike hybrid systems, on-grid solar systems are not able to function or generate electricity during a blackout due to safety reasons. Since blackouts usually occur when the electricity grid is damaged; If the solar inverter was still feeding electricity into a damaged grid it would risk the safety of the people repairing the fault/s in the network. Most hybrid solar systems with battery storage are able to automatically isolate from the grid (known as islanding) and continue to supply some power during a blackout.
Off-Grid System:

An off-grid system is not connected to the electricity grid and therefore requires battery storage. Off-grid solar systems must be designed appropriately so that they will generate enough power throughout the year and have enough battery capacity to meet the home’s requirements, even in the depths of winter when there is generally much less sunlight.
The high cost of batteries and off-grid inverters means off-grid systems are much more expensive than on- grid systems and so are usually only needed in more remote areas that are far from the electricity grid.
Hybrid System:

Modern hybrid systems combine solar and battery storage in one. Due to the decreasing cost of battery storage, systems that are already connected to the electricity grid can start taking advantage of battery storage as well.
This means being able to store solar energy that is generated during the day and using it at night. When the stored energy is depleted, the grid is there as a back up, allowing consumers to have the best of both worlds.